Have you ever spent any time looking at the Mandelbrot set? I don’t mean a cursory glance, I mean really contemplated it?
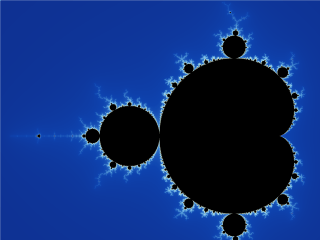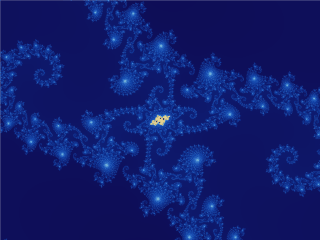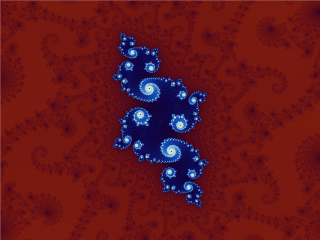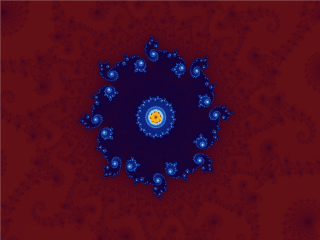
And I don’t even mean the fancy coloured versions, just the straight black-and-white one (see image on right)?
It is really far more interesting than it looks…
================
At first glance it just looks like a prickly pear gone wrong, so what is so interesting?
Well, remember this graph shows a set, that is to say it divides numbers into two groups, those inside the set, and those outside.
You could easily create such a set with circle – you can define the co-ordinates inside the circle is ‘in’ the set and that which is outside the circle outside the set. Such a set can be defined in a sentence: it is all points c less than the distance r from the origin.
The Mandelbrot set is just the same – a shape that divides space into two regions – in the image, the black area shows the numbers in the set, and the white area show the numbers out of the set. The only difference from a circle is that the Mandelbrot shape is more wiggly.
It equation is not much longer to define:
It is all numbers c, where if you square the number, then add the number, then square the result and add the number again, then repeat, it does not tend to infinity.
So zero is in the set, if you square it, then add it, it is still zero.
How about 1? No, it will run off: 1,2,3, 4, …
-1, on the other hand, squared, is 1, then added, goes to zero, where it will get stuck: -1, 0,0,0…
Figuring out the contents of the set is however complicated. Bloody complicated. Infinitely complicated in fact, and one of the marvels of the mathematical world.
To get a feeling exactly how complex this set is, take a look at some animations in which you zoom in on the perimeter; you can google “fractal dive” for more…
[youtube=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fLrSapMYUlI]
You can choose what part of the set to zoom into yourself, if you want, here: http://www.h-schmidt.net/MandelApplet/mandelapplet.html
It seems that one simple sentence has been able to define an infinitely complex boundary, and begs some interesting questions: have we created a sort of universe? What is the information content of this set?
It makes my head hurt.
===============
The area of specific interest to me, is the relationship between the platonic ‘world of maths’ and the real world; so are there parallels between such complexity in the world of numbers and the real world?
Clearly fractals sometimes have similarity to things in the real world – such as crystals, feathers and broccoli florets. We see many reminders of complex structure in the real world, and it brings me to think of the earth as a sort of giant 3-d fractal – where the solid matter is ‘in the set’ and the gas of the atmosphere and the vacuum of space is “out of the set”.
We can see that the interface, the earth’s surface, also has complex structure, including such things as crystal caves or the lining of your lungs – and like with the Mandelbrot, we also seem able to zoom in to many levels.
However, just as there are no perfect spheres in the real world, there are no perfect fractals, and it seems that the structure falls apart once we get to subatomic levels of zoom (or does it?)
Some part’s of the earth’s interface are fractal-like due to the iterative nature of their construction (tree growth, crystal growth, sea-shells, etc.), and you can see that a simple rule of “branching” in a plant can make a complex shape. However, some of the complexity, specifically organic and bio-chemistry, still seem different (to me anyway).
================
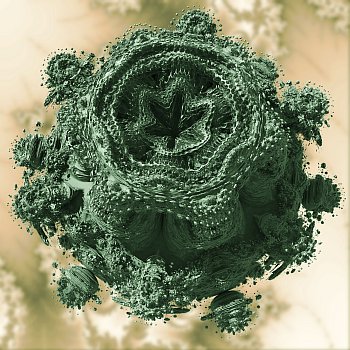
Now it turns out that my idea of the earth as a fractal with its skin as a complex interface can be more closely matched to the newly invented (discovered?) “Mandelbulb”, the amazing 3-d set. The interesting story of their development is told by one of their key developers, Daniel White, here.
The Mandelbulb is amazing because, as with many other fractals, you can zoom in and see ever more fascinating detail, and with incredible variation, and if you zoom into it continuously it would not be unlike zooming in on planet earth using Google Earth.
This excellent video below shows the idea of zooming into the Earth off well (it seems to be derived from a book I happen to have called “Powers of Ten“).
[youtube=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9BjHvwSvpOw]
So of course, you can do a similar trick on the Mandelbulb:
[youtube=http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LxsniUIVfEM]
Enough said!